Aka: Revenue Strategies - the Foundation for CRO Success
In a recent confidential interview, a CEO shared his thoughts about the next 12 months: "We believe we will achieve our revenue and profit goals over the next 12 months with our current resources. We have the right team, the latest software and tools, effective processes, remarkable products & services, strong branding and a unique value proposition." He went on to admit “… but we are not achieving our revenue and profit goals and we are still unsure why.”
The proper revenue strategy aligns marketing, sales, and customer experience teams around a singular goal: drive profitability. Without a strategic roadmap, healthy and sustained growth simply cannot flourish, which is why organizations put so much emphasis on the planning process. In fact, studies reveal that tightly-aligned sales and marketing functions result in an average of 36% higher customer retention rates and 38% higher sales closing rates, than their more loosely aligned counterparts.
Unraveling such a puzzle to understand what is ‘broken’ has us first visiting the revenue strategy. Choosing a revenue strategy impacts all other aspects of planning and whether goals are achieved.
Download this article as a pdf here >
The best revenue strategy requires answers
to these essential questions:
Strategy & Goals
1. What are our overall business goals?
2. How effective is our current strategy?
Profit
3. Are we profitable, or as profitable as we should be?
Definition
4. How do we define our complete sales process and sales funnel?
5. How do we define success?
Measure Metrics
6. How do we measure the effectiveness of our sales process?
7. How do we measure the effectiveness of each stage of our sales process?
8. How are sales results measured?
9. What is our ROI on our marketing efforts?
10. What is the ROI on our sales efforts?
11. What is our current customer acquisition cost (CAC)?
Optimization
12. Are we using and maximizing the resources we have?
13. How do we improve conversion ratios during the sales process?
Costs
14. Are there opportunities to lower cost with a more effective strategy?
People Management
15. What management systems are required?
16. How much time is dedicated to sales and sales management by key leaders or managers?
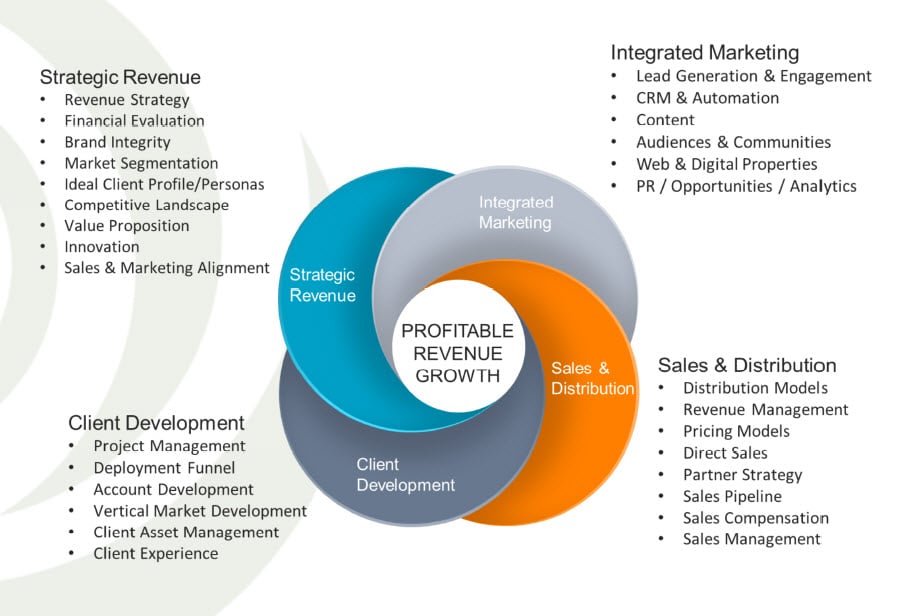 Source: Our Approach & Methodology to Increase Profitable Revenue
Source: Our Approach & Methodology to Increase Profitable Revenue
Download this article as a pdf here >
Which Revenue Strategy?
Determining which revenue strategy to pursue is often the most difficult part when planning corporate objectives. The sea of empty space that stares back at executives from a blank whiteboard can deafen strategic brainstorming attempts with its silence.
Knowing which questions to ask and variables to consider is the most effective way to broach the subject of strategic revenue planning. Questions like,
Which sales and marketing opportunities are available to us immediately?”
What are our most valuable assets?”
Are the right people in place to execute our short-term and long-term goals?”
...can get the conversation started.
Once the discussion is underway, the revenue strategies below can inspire your team to find the best growth avenues that utilize your assets and opportunities effectively.
To enable you to meet your organization's revenue/profit goals and offer you starting point with a revenue strategy, here are 21 Revenue Strategies to fill your whiteboard and get you started:
(1) Increasing Marketing Investments
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with budget allocation imbalances and those being outpaced by competitors in terms of marketing funding.
Considerations:
- Additional web creative and collateral needs
- Increased lead volume to sales teams
Scaling up marketing investments can generate more leads, which is a direct revenue driver. However, flooding the pipeline with more sales opportunities is only an effective strategy for organizations where the sales staff is prepared to handle this influx, which is why marketing cannot thrive in a vacuum. To be successful, marketing and sales teams need to communicate openly about current undertakings, upcoming plans, and overall objectives.
(2) Changing Sales Compensation Plans
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with excess sales team capacity or inefficient compensation and bonus plans.
Considerations:
- Added demands on account representatives
- Potential for undesirable revenue outcomes
In instances where leads are plentiful, ineffective compensation plans can stymie growth by failing to encourage sales teams to capitalize all available opportunities. Sales staff that are not motivated with financial, social, and other incentives will underperform, leaving potential revenue on the table. However, some revised compensation plans actually encourage undesirable outcomes like selling higher volumes of shorter contracts, which is why revenue implications must be considered when drafting compensation structures.
(3) Expanding Brand Awareness
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Startups and regionally successful companies.
Considerations:
- Sales pipeline growth implications
- Development of supporting marketing resources
- Ability to control the subsequent brand conversation
The adage that “you can only sell to consumers who know your company exists” still resonates. By focusing on overall branding, organizations can increase brand awareness throughout the market to aid in lead generation. While this is a less immediate strategy than other marketing efforts, it is still directly correlated with increasing revenue.
(4) Repositioning the Brand
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Legacy brands with declining or plateauing growth.
Considerations:
- Marketing channel expansion
- Increasing marketing support needs
- Market research to identify brand differentiation opportunities
In organizations where brand history has a solidified perception, there is a clear opportunity through rebranding to increase future revenue streams. This is especially salient when changes in audience demographics and psychographics necessitate a corresponding transformation by legacy brands to stay relevant.
As an example, fast food companies like Wendy’s and McDonald’s have invested millions in marketing campaigns over the last several years aimed at repositioning their brands as “healthy” and “fresh.” This rebranding tactic is aimed at appealing to modern consumers that have indicated that they value quality ingredients and more varied menu options, as well as convenience.
(5) Adopting a Premium Pricing Strategy
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with undifferentiated and value-priced offerings.
Considerations:
- Product research to drive innovation
- Demonstrating brand value
- Strategy for re-launching offerings
Providing additional value and raising prices is a strategic move that can positively affect the perception of both an organization and its offerings. Utilizing premium pricing and justifying the increase through supporting marketing and sales support can result in revenue lift. Furthermore, it can increase revenue by without a need to substantially vary offerings.
(6) Incorporating Discounted Pricing Tactics
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with price-sensitive target audiences.
Considerations:
- Effect on sales compensation plans
- Need for additional marketing collateral
- Alignment with overall revenue goals
Lowering prices can undercut the competition, resulting in a market penetration strategy that drives revenue. However, reducing prices is not the only way to discount products. Organizations can also achieve revenue growth by bundling offerings to provide more value at a discounted rate, offering product rebates, and changing shipping and handling pricing structures. Providing seasonal discounts and purchase timing discounts is another way to incentivize conversions through reduced pricing. Organizations can also pare down existing product functionality to offer more budget-friendly versions of the same products to increase sales across a wider demographic.
(7) Expanding Distribution Channels
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with consistent revenue and well-executed sales plans.
Considerations:
- Legal partnership agreement considerations
- Availability of current products and future product capacity
- Need for increased staffing (especially among specialized roles)
Stepping out of existing distribution channels to embrace a new selling strategy is a way to boost revenue from existing products by getting them in front of previously unreached consumers. Selling via retailers, distributors, ecommerce sites, direct mail, and wholesalers encompasses a wide array of potential channels where consumers can shop.
For online businesses, social selling is another possible method to expand distribution channels, by allowing sales of products directly from the social platforms where consumers are already interacting with the brand.
(8) Developing Cooperative Sales Agreements
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations that can leverage strong brand recognition to offer value to potential partners.
Considerations:
- Alignment with the overall organizational mission
- Mutually beneficial reciprocity expectations
- Additional contract and clause requirements
Reciprocal selling agreements are another way to introduce offerings to consumers through another channel. Amazon began using this strategy recently when they acquired Whole Foods as an extension of their Amazon Fresh service to provide quick delivery of groceries to Amazon Prime members in select cities. This type of reciprocity is a victory for both Amazon and Whole Foods, which can increase revenue margins for both brands through cooperation.
(9) Diversifying Offerings
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with established offerings and well-honed research and development capabilities.
Considerations:
- Assessment of the possibility for sales cannibalization
- Strategic marketing resources to align and promote new offerings
- Understanding of new industry competition variables
- Additional need for experienced sales personnel
Finding lucrative complementary offerings for top-selling products and services can be a shrewd way to encourage revenue growth. Identifying consumers’ needs and filling in the gaps with offerings that help sell main revenue drivers, boosts overall revenue by increasing average customer lifetime value.
(10) Repositioning Offerings
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with versatile offerings that can fulfill an array of needs or provide flexible solutions for consumers.
Considerations:
- Additional marketing resources
- Ongoing specialized sales training needs
- Audience research to identify product use capabilities
For products and services that can be used by consumers to fulfill multiple needs or use-case scenarios, repositioning offerings to target each of these uses and audiences is a clever way to increase revenue. By targeting specific uses individually, marketing and sales messaging can be customized to address specific needs, wants, and apprehensions. The result is a more effective and adaptable selling strategy.
(11) Modernizing Legacy Offerings
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Brands with stagnant offerings and organizations with an aversion to change.
Considerations:
- Preservation of existing offerings to retain existing customers, where appropriate
- Brand repositioning potential
- Increased marketing collateral demands
- Assessment of channel expansion possibilities
- Potential sales retraining requirements
Replacing or updating traditional products and services is a sound way to use legacy offerings to increase revenue. Using previously successful offerings as the basis to launch a growth strategy provides a revenue safety net to safeguard against possible failures.
(12) Securing Recurring Revenue
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with offerings conducive to subscription-based usage.
Considerations:
- Increased payment system demands
- Additional accounts receivable staffing
- Increased focus on customer experience
Creating recurring subscriptions or ongoing contracts is another way to use existing offerings to drive revenue. By taking the onus away from consumers to decide when to purchase again, organizations can both secure future revenue and increase the likelihood of developing brand loyal customers.
(13) Focusing on Product Penetration
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with brand loyal customers and a breadth of offerings.
Considerations:
- Additional staff needed to solidify customer relationships
- Specialized marketing tactics to engage existing customers
Unlike market penetration, which focuses on selling the same offerings to more consumers, product penetration aims to get existing customers to purchase more of an organization’s offerings. This means providing complementary products and services that customers can subsequently purchase, even after buying items that are not readily consumed. For some organizations this involves expanding offerings, whereas for others it involves engaging in mutually beneficial partnerships. In other instances, it simply requires pivoting an existing marketing strategy to convince consumers that they will benefit from taking advantage of other offerings as well.
(14) Increasing Customer Retention
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with a sizeable customer base and substantial post-sales support methodology.
Considerations:
- Shifting marketing emphasis from customer acquisition to retention
- Increased focus on customer experience
- Effect on sales team compensation and performance objectives
Retaining existing customers will always be more cost effective than acquiring new customers, which makes it an obvious revenue growth strategy. However, the nuances involved in achieving this objective require sales, marketing, and customer experience team buy-in. While marketing teams are typically open to changing their strategic focus towards supporting customer retention, sales teams often oppose the proposition due to concerns regarding compensation. Without a change to compensation structure to reward increases in customer lifetime value, sales teams are likely to act independently to protect their own interests. When collaborative buy-in is achieved, customer retention drives immediate revenue growth while simultaneously securing sustainable future growth by developing brand loyalty and advocacy.
(15) Dominating the Mobile Experience
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with an increasing mobile consumer base or target demographic.
Considerations:
- Technological upgrades needed to establish and maintain the mobile experience
- A complementary tech-savvy focus among employees
Encouraging ecommerce mobile shopping and utilizing app-based experiences are at the heart of a thriving mobile strategy. While some organizations are hesitant to enter the mobile arena due to the complexity of offerings or historically low-tech reputation of their industries, supporting mobile users is essential for growth in today’s economy. However, providing a haphazard mobile experience is often worse than not offering one at all, which means that the right technological savvy and support must comprise an effective mobile strategy.
(16) Nurturing Brand Advocates
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with brand loyal customers that are willing to engage.
Considerations:
- Implementation of customer rewards programs and incentives
- Engagement tactics that meet customers where they thrive
Fostering brand advocacy is both a revenue strategy and a reputation management strategy. Nurturing customer relationships encourages brand loyalty, increasing revenue figures organically from the brand advocates themselves and their personal networks. Brand advocates are more likely to defend the brand in times of turmoil or crisis, making them an indispensable asset. However, brand advocate creation is not simply achieved through offering purchase incentives and other superficial tokens. It requires the kind of strategic planning that weaves through every customer experience from sales and marketing to technical support and billing. Building brand advocates also involves meeting customers on their own terms – on the platforms and at the moments when they want to engage.
(17) Developing New Partnerships
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with a collaborative spirit that can benefit from outsourcing functions or capabilities.
Considerations:
- Internal staffing implications
- Availability of complementary organizations willing to engage in partnerships
- Legal considerations for partnership agreements
- Effect on future hiring
Pairing with other organizations expands an organization’s capabilities and sphere of influence without having to invest in additional in-house resources. While many business leaders may cringe at the thought of relinquishing control, the smartest executives understand the value of partnership. Refusing to enter into strategic partnerships can hamstring growth faster than any other mistake, which is why from a growth perspective, the only questions should be when to establish partnerships and with whom.
(18) Engaging with Industry Influencers
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations where well-known personalities can be leveraged to encourage revenue growth.
Considerations:
- Adapting social media efforts
- Risk assessment of aligning with third-party individuals
- Legal considerations of social collaboration
Influencer marketing has been a hot topic in recent years due to its effectiveness in building industry authority and driving revenue. Collaborating with respected industry experts can be an effective way to build brand awareness, acquire new customers, and impress existing customers. However, working with independent third-party individuals also carries some risk, which means that legal implications should be considered before pursuing this strategy, especially in highly-regulated industries.
(19) Expanding Geographic Reach
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Brands with a limited geographic territory and demographic potential to expand.
Considerations:
- Supply chain and logistics considerations
- Additional staffing required at all levels of the business
- Individual market preference variations
- New market barriers to entry
Expanding geographically is one of the simplest and yet most complex ways to grow revenue. This method is easy to conceptualize and difficult to execute properly, which is why organizations undertake such long planning processes before opening additional franchises, distribution centers, warehouses, retail venues, and so on. Considering regional preferences, opportunities, and barriers is a mammoth task that requires the right strategic analysis by highly experienced professionals. The result when expansion is done successfully, however, can be a substantial windfall.
(20) Offering Additional Payment Options and Terms
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations stifled by existing payment options and sales terms.
Considerations:
- Financial feasibility of payment expansion
- Legal considerations of extending payment terms
Opening up payment options and flexibility with payment terms can allow an organization to close additional sales that would otherwise have been unavailable. However, doing so often comes at a cost – either in the form of initial technology investments or the potential for bad debt when terms are not met as planned.
(21) Eliminating Bad Customer Relationships
Ideal Revenue Strategy for:
Organizations with revenue constriction due to unprofitable or toxic customer relationships.
Considerations:
- Social implications of eliminating customers
- Legal limitations on existing contracts
While it may be a controversial strategy, firing unprofitable customers is another way to improve revenue numbers. By pruning deadweight from the customer base, an organization can more effectively focus resources on profitable customer relationships. In 2007 Sprint famously utilized this strategy to cancel subscriptions for customers that were tying up support channels. They reasoned that they could not properly support more profitable customer contracts due to the burden that “bad customers” were placing on the system. This move came amidst a high customer turnover trend that Sprint was looking to reverse.
Download this article as a pdf here >
The proper revenue strategy aligns marketing, sales, and customer experience teams around a singular goal: drive profitability. Without a strategic roadmap, healthy and sustained growth simply cannot flourish, which is why organizations put so much emphasis on the planning process.
The right strategy will ensure you achieve your revenue and profit goals. It will be a foundation for selecting and developing the right team, the right software and tools, developing effective processes, remarkable products & services. The process begins by creating the right revenue strategies to align and leverage your sales, marketing, and customer experience teams.
If you are in a situation where you have the right people, resources and processes in place and are unsure why you are not achieving your revenue and profit goals, I welcome you to contact me here, or by phone or email. We can talk about any of the strategies listed above or another that is of interest to you.
As you begin to formulate ideas and a plan, feel free to use our B2B Business Growth Library.

